|
Anthranilic acid
CAS number 118-92-3

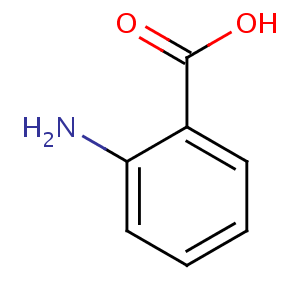
Anthranilic acid is the organic compound with the formula C6H4(NH2)CO2H.
This amino acid is white solid when pure, although commercial samples
may appear yellow. The molecule consists of a benzene ring with two
adjacent functional groups, a carboxylic acid and an amine. Because
these two groups are polar, this organic compound is highly soluble in
water. It is sometimes referred to as vitamin.
Properties
Molecular formula C7H7NO2
Molar mass 137.14 g mol−1
Density 1.4 g/cm3
Melting point
146-148 °C
Boiling point
Sublimes
Solubility in water 5.7 g/L (25 °C)
Solubility Hot water
Hazards
MSDS External (html)
R-phrases R36 R37
S-phrases S26 S39
Flash point >150 °C
Synonyms:
o-Aminobenzoic acid; 2-Carboxyaniline; Anthranilic acid; Benzoic acid,
o-amino-; Kyselina o-aminobenzoova [Czech]; Anthranilate; o-Carboxyaniline;
ortho-Aminobenzoic acid; 2-Aminobenzoic acid; ANTHRANILIC ACID; Benzoic
acid, 2-amino-; Kyselina anthranilova [Czech]; 1-Amino-2-carboxybenzene;
2-Aminobenzoate; Caswell No. 033G; Vitamin L1; BRN 0471803; o-Anthranilic
acid; NCI-C01730; AI3-02408
Uses
Anthranilic acid is used as an intermediate for production of dyes,
pigments, and saccharin. It and its esters are used in preparing
perfumes to imitate jasmine and orange, pharmaceuticals (loop diuretics
eg. furosemide) and UV-absorber as well as corrosion inhibitors for
metals and mold inhibitors in soya sauce.
Anthranilic acid can be used in organic synthesis to generate the
benzyne intermediate.
|
TYPES OF HAZARD /
EXPOSURE |
ACUTE HAZARDS /
SYMPTOMS |
PREVENTION
|
FIRST AID / FIRE
FIGHTING |
|
FIRE |
Combustible. Gives off
irritating or toxic fumes (or gases) in a fire.
|
NO open flames.
|
Powder, water spray,
foam, carbon dioxide.
|
|
EXPLOSION
|
Finely dispersed
particles form explosive mixtures in air.
|
Prevent deposition of
dust; closed system, dust explosion-proof electrical equipment and
lighting.
|
|
|
EXPOSURE
|
|
|
|
|
Inhalation
|
|
Local exhaust or
breathing protection.
|
Fresh air, rest.
|
|
Skin |
|
Protective gloves.
|
Rinse and then wash skin
with water and soap.
|
|
Eyes |
Redness. Pain.
|
Safety spectacles
|
First rinse with plenty
of water for several minutes (remove contact lenses if easily
possible), then take to a doctor.
|
|
Ingestion
|
|
Do not eat, drink, or
smoke during work.
|
Rinse mouth. Give one or
two glasses of water to drink. Seek medical attention if you feel
unwell |
| |
|
Note /Government
Notification: These chemicals are designated as those that are used
in the manufacture of the controlled substances and are important to
the manufacture of the substances. For any (Control Substance)
products Import and Export *** subjected to your country government
laws /control substance ACT.
Information: The information on this web page is provided to help
you to work safely, but it is intended to be an overview of hazards,
not a replacement for a full Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS). MSDS
forms can be downloaded from the web sites of many chemical
suppliers. ,also that the information on the PTCL Safety web site,
where this page was hosted, has been copied onto many other sites,
often without permission. If you have any doubts about the veracity
of the information that you are viewing, or have any queries, please
check the URL that your web browser displays for this page. If the
URL begins "www.tajapi.com/www/Denatonium Benzoate.htm/" the page is
maintained by the Safety Officer in Physical Chemistry at Oxford
University. If not, this page is a copy made by some other person
and we have no responsibility for it.
The Controlled Substances Act (CSA) was enacted into law by the
Congress of the United States as Title II of the Comprehensive Drug
Abuse Prevention and Control Act of 1970.[1] The CSA is the federal
U.S. drug policy under which the manufacture, importation,
possession, use and distribution of certain substances is regulated.
The Act also served as the national implementing legislation for the
Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs |
|
|
|
|









