
|
Pseudoephedrine hydrochloride
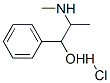
|
Molecular Formula
: C10H16ClNO
Molecular Weight : 201.69
CAS No. : 345-78-8
Chemical Name:
1. (1S,2S)-2-Methylamino-1-phenyl propan-1-ol, Hydrochloride
2. Benzenemethanol, a-[1-(methylamino)ethyl]-, [S-(R*,R*)],
Hydrochloride
Synonyms:
(+)-PSI-EPHEDRINE HYDROCHLORIDE;PSI-EPHEDRINE
HYDROCHLORIDE;PSEUDOEPHEDRINE HCL;PSEUDOEPHEDRINE HCL,
(+)-1S,2S-;(+)-PSEUDOEPHEDRINE HYDROCHLORIDE;PSEUDOEPHEDRINE
HYDROCHLORIDE;a)]-;alpha-(1-(methylamino)ethyl)-,hydrochloride,(s-(r*,r*))-benzenemethano;benzenemethanol,alpha-[1-(methylamino)ethyl]-,hydrochloride,[s-(theta,thet;hydrochloride,l-(+)-pseudoephedrin;l(+)-
pseudoephedrinehydrochloride;novafed;sinufed;sudafed;symptom2;tussaphed;D-PSEUDOEPHEDRINE
HYDROCHLORIDE;D-ISOEPHEDRINE HYDROCHLORIDE;ISOEPHEDRINE
HYDROCHLORIDE;(1S,2S)-2-(METHYLAMINO)-1-PHENYL-1-PROPANOL
HYDROCHLORIDE
Specifications :
| 1. |
Description : |
Fine, white to
off white crystals or powder. |
| 2. |
Identification : |
a ) Infrared
spectrum of sample is concordant with the
reference spectrum.
b) A solution of sample responds to the test for chloride |
| 3. |
Melting
range : |
Between 182° and
186°C; the range between beginning
and end of melting does not exceed 2°C |
| 4. |
Specific
rotation : |
Between + 61.0°
and + 62.5° (5 % solution in water) |
| 5. |
Solubility
: |
Very soluble in
water and freely soluble in alcohol. |
| 6. |
pH : |
Between 4.6 and
6.0 (5 % solution in water) |
| 7. |
Ordinary
impurities : |
NMT 2.0 % |
| 8. |
Residue on
ignition : |
NMT 0.1 % |
| 9. |
Loss on
drying : |
NMT 0.5 % |
| 10. |
Organic
volatile impurities : |
Must pass the test |
| 11. |
Assay : |
Between 98.0 % and 100.5 % (
dried basis ) |
Therapeutic indications : Decongestant Packing :
Packed in double lined polyethylene bags in 25 kg fiber drums.
Storage : Store below 35°C. |
Pseudoephedrine is a
sympathomimetic amine commonly used as a decongestant. The salts
pseudoephedrine hydrochloride and pseudoephedrine sulfate are found in
many over-the-counter preparations either as single-ingredient
preparations, or more commonly in combination with antihistamines,
paracetamol (acetaminophen) and/or ibuprofen. Sudafed is a trademark for
a common brand which contains pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, though
Sudafed PE does not. Cirrus contains pseudoephedrine in conjunction with
cetirizine (an antihistamine).
Unlike antihistamines, which relieve multiple allergic symptoms by
acting as antagonists at histamine receptors, pseudoephedrine primarily
relieves nasal congestion commonly associated with colds or allergies.
The advantage of oral pseudoephedrine over topical nasal preparations,
such as oxymetazoline, is that it does not cause rebound congestion
(rhinitis medicamentosa); however, it is more likely to cause adverse
effects including hypertension.
Pseudoephedrine is being phased out as an over-the-counter drug in some
countries and replaced by less effective.
Chemistry
Pseudoephedrine is a phenethylamine, and a diastereomer of ephedrine.
Pseudoephedrine is a chiral molecule, meaning it occurs in both
"left-handed" and "right-handed" configurations which are not
superimposable.
Pseudoephedrine is the International Nonproprietary Name (INN) of the
(1S,2S)- diastereomer of ephedrine (which has 1R,2S- configuration).
Other names are (+)-pseudoephedrine and D-pseudoephedrine.
L-Pseudoephedrine, also known as (-)-(1R,2R)-pseudoephedrine or (-)-pseudoephedrine,
is the optical isomer of D-pseudoephedrine. It has fewer side-effects,
fewer central nervous system (CNS) stimulatory effects, does not reduce
to D-methamphetamine (which is the enantiomer used as a recreational
drug), and yet it retains its efficacy as a decongestant.[citation
needed] However, the patent holder for L-pseudoephedrine (Pfizer/Warner-Lambert)[has
not yet sought or received government approval for its sale to the
public.
Clinical uses
Indications
Pseudoephedrine is indicated for the treatment of:
* nasal congestion
* sinus congestion
* Eustachian tube congestion.
Pseudoephedrine is also indicated for vasomotor rhinitis, and as an
adjunct to other agents in the optimum treatment of allergic rhinitis,
croup, sinusitis, otitis media, and tracheobronchitis.
Adverse effects
Common adverse drug reactions (ADRs) associated with pseudoephedrine
therapy include: CNS stimulation, sleeplessness, nervousness,
excitability, dizziness and anxiety. Infrequent ADRs include:
tachycardia and/or palpitations. Rarely, pseudoephedrine therapy may be
associated with hallucinations, arrhythmias, hypertension, seizures and
ischemic colitis;as well as severe skin reactions known as recurrent
pseudo-scarlatina, systemic contact dermatitis, and nonpigmenting fixed
drug eruption.Pseudoephedrine, particularly in high doses, may also
cause episodes of paranoid psychosis.It has also been reported that
pseudoephedrine, amongst other sympathomimetic agents, may be associated
with the occurrence of stroke.
 Note:
These API/ chemicals are designated as
those that are used in the manufacture of the controlled substances and
are important to the manufacture of the substances. For any (Control
Substance) products Import and Export *** subjected to your country
government laws /control substance ACT. Note:
These API/ chemicals are designated as
those that are used in the manufacture of the controlled substances and
are important to the manufacture of the substances. For any (Control
Substance) products Import and Export *** subjected to your country
government laws /control substance ACT.
Note /Government Notification:
These chemicals are designated as those that are used in the manufacture
of the controlled substances and are important to the manufacture of the
substances. For any (Control Substance) products Import and Export ***
subjected to your country government laws /control substance ACT.
Information: The information on this web page is provided to help you
to work safely, but it is intended to be an overview of hazards, not a
replacement for a full Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS). MSDS forms can
be downloaded from the web sites of many chemical suppliers. ,also that
the information on the PTCL Safety web site, where this page was hosted,
has been copied onto many other sites, often without permission. If you
have any doubts about the veracity of the information that you are
viewing, or have any queries, please check the URL that your web browser
displays for this page. If the URL begins "www.tajapi.com/www/Denatonium
Benzoate.htm/" the page is maintained by the Safety Officer in Physical
Chemistry at Oxford University. If not, this page is a copy made by some
other person and we have no responsibility for it.
The Controlled Substances Act (CSA) was enacted into law by the Congress
of the United States as Title II of the Comprehensive Drug Abuse
Prevention and Control Act of 1970.[1] The CSA is the federal U.S. drug
policy under which the manufacture, importation, possession, use and
distribution of certain substances is regulated. The Act also served as
the national implementing legislation for the Single Convention on
Narcotic Drugs.
|
|










